Always wondered how your smartphone always knows exactly where you are, or how delivery companies manage to get packages to your doorstep with pinpoint accuracy?
It's all possible because of a single experiment conducted by the United States Navy in the 1970's and we all know it today as GPS.
At AutoPi, we rely on GPS to enhance our devices, helping customers to navigate vehicle fleets with ease. But GPS is more than just a navigation aid—it's a critical technology that shapes everything from emergency responses to fitness tracking.
In this article, we'll take a look into how GPS works, its indispensable role in modern technology, and how it's evolving to offer even more.
Let's get started.
What is GPS?
GPS, which is short for Global Positioning System, is a network of about 31 satellites orbiting Earth at all times. Invented by the U.S. Department of Defense in the 1970s, it was initially intended for military use but was opened to the public in the 1980s. Today, it's a universal service that supports countless applications across the globe.
So, what does GPS stand for? As mentioned, GPS stands for Global Positioning System, a term that encompasses the technology's broad capabilities beyond mere location tracking. It provides two key services:
-
Location Services: It determines the precise location of a GPS receiver—whether it's in your phone, your car, or a shipping container—by calculating its distance from multiple satellites.
-
Timing Services: GPS provides extremely accurate time measurements, which are crucial for systems like financial transactions and power grids.
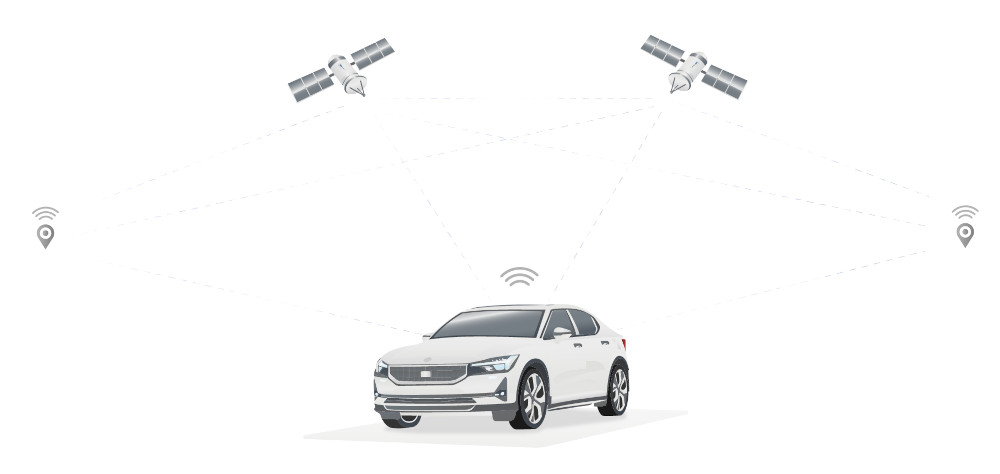

Key Components of GPS
GPS seems like it's only about getting from point A to B, but it's actually built on a complex, yet fascinating system made up of three parts:
-
The Space Segment: Picture this—a constellation of about 31 satellites spinning around Earth. Each one is constantly sending signals down to us, loaded with precise time-stamps from their onboard clocks. These are the stars of the GPS show, zipping through space to keep us on the right path.
-
The Control Segment: Back on Earth, there's a whole network of ground-based stations keeping an eye on these satellites. These stations make sure every satellite is working correctly and beaming back accurate data. It’s like having mission control in a sci-fi movie, constantly monitoring and adjusting to keep everything running smoothly.
-
The User Segmenet: This is where you and I come in. Every device with GPS—like your smartphone, your car's navigation system, or even a farmer’s tractor—is part of this segment. These devices catch the signals from the satellites and use them to figure out exactly where they are.

All these components work together seamlessly to give us accurate location and timing, which are essential not just for simple tasks like finding the nearest coffee shop, but for everything from overseeing vast farming operations to navigating construction sites, and even coordinating emergency responses or conducting scientific research.
For example, with AutoPi devices, we've taken GPS capabilities further by incorporating A-GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo systems alongside the traditional GPS.
This means that an AutoPi-equipped vehicle can achieve pinpoint accuracy in location tracking, and also, calculate the distance the vehicle has driven on a specific day. This integration ensures that the users have access to the most precise and reliable positioning data.
How Does GPS Works?
GPS might feel like a bit of modern magic, but it's actually all about timing and location.
Here’s how it works, broken down into easy-to-understand steps:
-
Sending Signals: GPS satellites up in space constantly send out signals. These signals tell us the satellite's location and the exact time they were sent. Imagine them zooming towards Earth at the speed of light, reaching devices like your smartphone or the GPS in your car.
-
Catching Signals: Your device listens for these signals from several satellites. This is the starting point for figuring out your location.
-
Measuring Distance: Your device checks how long each signal takes to reach it. Since the signals travel at light speed, timing them helps us figure out how far away each satellite is.
-
Pinpointing Location: With distances from multiple satellites, your device uses a method called trilateration to work out exactly where you are on Earth. It's like connecting the dots but in a very high-tech way.
-
Timing Everything: GPS isn't just about finding places. It’s also super important for synchronizing time across various technologies and applications.
-
Improving Accuracy: To get even more precise, GPS uses some cool tricks. Differential GPS (DGPS) helps correct any small errors by comparing the GPS signal to a known location on the ground. Assisted GPS (A-GPS) uses data from cellular networks to find your location faster.

GPS Coordinates
GPS coordinates help us pinpoint any location on Earth using latitude and longitude.
For instance, the coordinates for our office are 57.03621° N latitude and 9.93501° E longitude.
Latitude shows how far north or south from the equator a place lies, while longitude tells how far east or west it is from the prime meridian.
Here's how to find these coordinates on Google Maps:
-
Open Google Maps on your device or web browser.
-
Type "57.0621, 9.93501" into the search bar and hit enter.
-
Google Maps will zoom in on our office, showing you the location with a marker.
GPS Technology
Imagine the precision needed here—each satellite has an atomic clock that’s accurate to within a few billionths of a second. This pinpoint timing is crucial because even the tiniest errors can lead to big mistakes in distance calculations.
The signals are smart, too; they carry all sorts of information that help your GPS receiver figure out which satellite it's dealing with and how everything is moving.
The GPS network is made up of 31 operational satellites, each part of a carefully planned constellation that ensures you can always find your way, whether you’re hiking in the mountains or navigating city streets.
The satellites are from different generations, each improving on the last in terms of accuracy and reliability.
-
Block IIA: These were the early workhorses, launched between 1990 and 1997. None are operational today, but they set the stage for what was to come.
-
Block IIR: 6 are still in operation, launched from 1997 to 2004. They improved stability and monitoring capabilities.
-
Block IIR-M: There are 7 of these, introduced between 2005 and 2009. They brought new features like enhanced resistance to jamming—important for military uses.
-
Block IIF: 12 of these satellites are currently active. Launched between 2010 and 2016, they feature advanced atomic clocks and a new signal on the L5 frequency, boosting accuracy.
-
GPS III/IIIF: The latest models, with 6 operational. These started launching in 2018 and offer the best in signal reliability, accuracy, and a longer, 15-year lifespan. They also come equipped with features like laser reflectors and search & rescue payloads.
For more detailed information about each satellite generation, check out GPS.gov.
This diverse group of satellites ensures that GPS remains a reliable tool for everything from everyday navigation to supporting critical global infrastructure. However, as with all technology, there will always be problems.
Challenges of GPS systems
GPS is incredibly advanced, but it isn’t perfect. It faces several challenges that can distort its accuracy.
In cities, for instance, tall buildings and narrow streets can block or deflect GPS signals, a problem often referred to as "urban canyons." Weather events like heavy storms or solar disturbances can also delay signals as they pass through the atmosphere, leading to errors.
Additionally, multipath errors can happen when signals bounce off large objects such as buildings or cliffs before reaching the GPS receiver, distorting the calculated location.
Addressing these issues requires constant advancements in GPS technology and its processing techniques, highlighting just how crucial and complex this technology is in ensuring precise navigation and synchronization across numerous global systems.
Applications and Advantages of GPS
Understanding the challenges of GPS helps us appreciate just how crucial and versatile this technology is in our daily lives and industries. We use it everyday, whether it's for finding a new restaurant or the fastest route.
However, there is more to it.
Let's look into how GPS does more than just help us navigate.
-
Navigation and Transportation:
-
Personal Navigation: From guiding you to the nearest cafe to plotting a cross-country road trip, GPS is essential for personal travel.
-
Commercial Logistics: Shipping companies rely on GPS for real-time tracking of goods, optimizing delivery routes, and managing fleets, which helps in reducing operational costs and improving service delivery.
-
-
Safety and Emergency Services:
-
Rescue Operations: GPS plays a critical role in search and rescue operations by providing precise locations, drastically reducing response times and increasing the chances of success.
-
Disaster Management: During natural disasters, GPS data helps coordinate efforts by mapping affected areas and planning the logistics of relief operations.
-
-
Environmental Monitoring and Management:
-
Wildlife Tracking: Scientists use GPS to track animal movements, study their behaviors, and monitor populations, which is crucial for conservation efforts.
-
Climate Studies: GPS sensors help measure atmospheric conditions, contributing to weather forecasting and climate change research.
-
-
Agriculture:
-
Precision Farming: GPS enables farmers to practice precision agriculture, including accurate field mapping, soil sampling, and crop scouting. This leads to more efficient planting, fertilizing, and harvesting.
-
-
Construction and Infrastructure:
-
Site Management: In construction, GPS is used for surveying and mapping land, ensuring accurate and efficient project execution.
-
Infrastructure Maintenance: GPS helps in monitoring the structural health of buildings and other infrastructure, aiding in maintenance planning and safety checks.
-
-
Sports and Recreation:
-
Athletic Training: Athletes and coaches use GPS devices to measure performance metrics such as speed, distance, and movement patterns.
-
Outdoor Recreation: Hikers, bikers, and adventurers use GPS for trail navigation, ensuring they can explore safely without getting lost.
-
Each of these applications not only shows us the versatility of GPS but also highlights its benefits such as increased efficiency, improved safety, and better decision-making capabilities.
Whether it’s navigating the unknown, saving lives, or helping farmers yield better crops, GPS has become a cornerstone of modern technology, making our daily tasks easier and our professions more effective.

The Future of GPS
GPS technology is on the point of exciting advancements. Soon, we’ll see next-generation satellites with ultra-precise atomic clocks that dramatically improve location accuracy, reducing errors to mere centimeters and bolstering resistance to interference.
GPS is also integrating with global navigation systems like Europe's Galileo, Russia's GLONASS, and China's BeiDou, expanding coverage and ensuring reliable service worldwide. This is crucial for technologies such as autonomous vehicles and precision surveying.
Moreover, GPS is extending its reach into smart cities and the Internet of Things (IoT). It's streamlining urban traffic management, optimizing emergency services, and enabling smarter operations like drone deliveries and precision farming.
Additionally, improvements in systems like WAAS and EGNOS are boosting GPS signal quality, improving safety in sectors such as aviation. Meanwhile, the integration of artificial intelligence with GPS is transforming predictive analytics, improving everything from route optimization to traffic forecasting.
As these developments progress, GPS is set to become an even more integral part of our technological infrastructure, simplifying our lives and making our systems even smarter. We are genuinely very excited for what's to come!
Conclusion
GPS does far more than just help us navigate from point A to point B. Its reach extends across daily commutes, global logistics, emergency responses, and much more. With ongoing advancements in technology improving its accuracy and broadening its uses, GPS is set to play an even more crucial role in our lives.
As GPS continues to evolve, its profound impact on our world becomes increasingly clear. Whether it’s navigating through city streets, tracking shipments across continents, or synchronizing financial transactions globally, GPS remains a fundamental piece of modern technology.
Frequently Asked Questions About GPS
-
How accurate is GPS?
-
Under open skies, GPS usually pinpoints locations within about a 5-meter radius. With newer technologies like Real-time kinematic positioning (RTK) and Satellite Based Augmentation System (SBAS), we can get this down to just a few centimeters in ideal conditions.
-
-
Can GPS work without an internet connection?
-
Absolutely, GPS doesn't need the internet to work. It calculates your position using signals from satellites. But, if you’re using a map app or need live traffic updates, then yes, you’ll need internet for that data.
-
-
Is GPS available everywhere?
-
Yes, GPS coverage is truly global. The system’s satellite network ensures that you can access GPS services anywhere on the planet.
-
-
Does weather affect GPS accuracy?
-
Certain weather conditions can interfere with GPS signals as they travel from the satellites to us. Things like heavy clouds or solar storms can cause disruptions, but advances in technology are reducing these issues.
-
-
What's the difference between GPS and A-GPS?
-
Regular GPS relies solely on satellite signals for navigation. Assisted GPS, or A-GPS, boosts GPS by using cellular data to improve the start-up speed and accuracy, especially helpful where satellite signals are weak.
-
Interested in learning more about how AutoPi leverages GPS technology? Visit our website to discover the innovative ways we're integrating GPS Fleet Tracking into our AutoPi devices and how it could benefit you.