The OBD, or On-Board Diagnostic port, is essential for diagnosing vehicle issues. The OBD2 port, a more advanced version of OBD1, offers enhanced diagnostic capabilities. At AutoPi, we provide resources to help you locate and use the OBD2 port effectively, ensuring you can maintain your vehicle’s health efficiently.
What Is an OBD2 Port?
The OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) port is a standardized 16-pin diagnostic interface found in most vehicles manufactured from 1996 onwards. It serves as a direct gateway to the vehicle’s onboard computer systems, providing access to real-time data, diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and system status information across various electronic control units (ECUs).
Physically, the OBD2 port is a trapezoidal socket typically located beneath the dashboard, within easy reach of the driver's seat. This placement is mandated by regulation to ensure accessibility for emissions testing and general diagnostics.
Functionally, the OBD2 port allows mechanics, fleet managers, developers, and car owners to connect scan tools, telematics devices, or custom hardware to communicate with the vehicle's internal network. Through this interface, users can retrieve error codes, monitor sensor outputs (such as engine load, fuel trim, or coolant temperature), reset warning lights, and even perform system readiness checks.
Although primarily used for emissions-related diagnostics, modern tools can leverage the port for much broader purposes, such as predictive maintenance, performance monitoring, fleet tracking, and remote control applications. The OBD2 protocol supports several communication standards, including ISO 15765 (CAN), ISO 9141-2, SAE J1850, and others, depending on the vehicle make and model.
In short, the OBD2 port is a vital access point for understanding and managing the internal state of today’s increasingly complex vehicles.
OBD2 Port Location
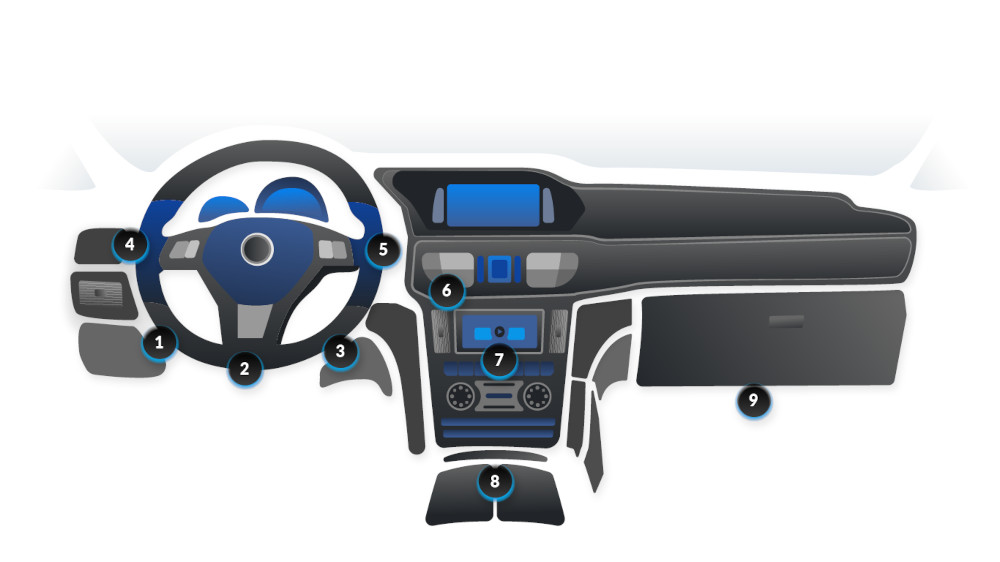
The location of the OBD2 port can vary by vehicle model, but it's commonly found within the driver's reach, often under the dashboard and near the steering wheel for easy access without tools. To find the exact location, check your vehicle's owner's manual or use an online OBD port finder.

See the image below for possible placements:

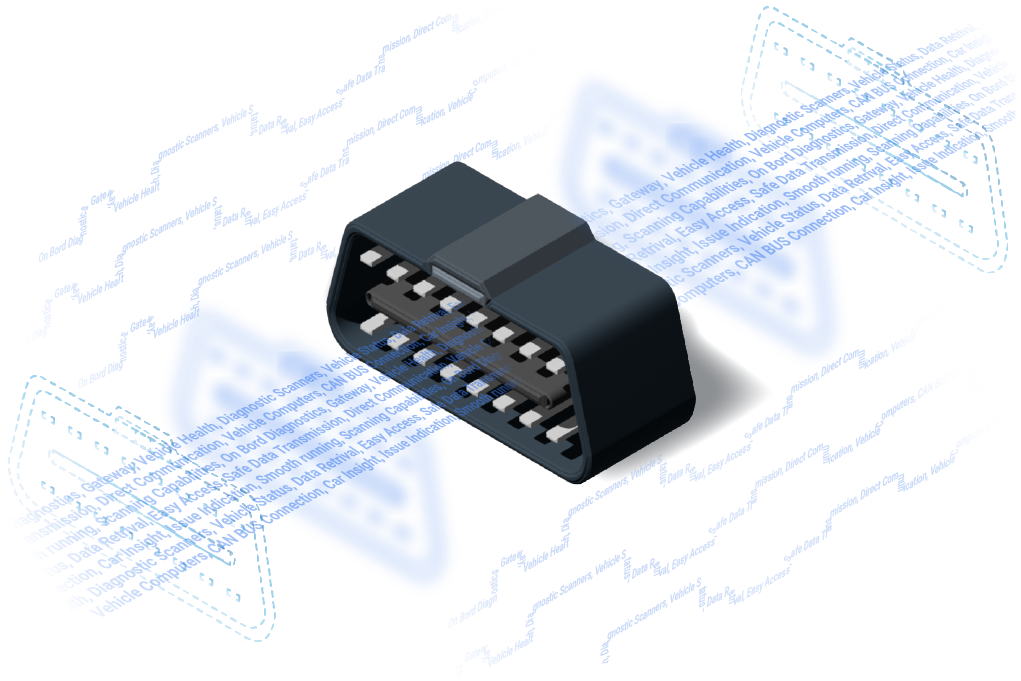
The OBD2 Connector and Pinout
The OBD2 connector allows for easy data retrieval from your vehicle. The AutoPi device is a male connector interfaces with the universal female OBD2 16-pin (2x8) J1962 connector. Unlike the OBD1 connector, often found near the hood, the OBD2 connector is typically within 2 feet of the steering wheel.

Quick Overview of the OBD2 Port Pinouts
The OBD2 port features a configuration of 16 pins, each with a unique role:
-
Pins 4 and 5: Provide grounding for safe and accurate data transmission.
-
Pins 2 and 10: Communicate with the SAE J1850 BUS+ for direct communication with the vehicle's main computer.
-
Pins 6 and 14: Connect to the CAN bus, crucial for many diagnostics processes as outlined by the ISO 15765-4 standard.
Why Is the OBD2 Port Important?
The OBD2 diagnostic port is essential for gaining insights into the car's engine, emission system, and more. It allows for comprehensive self-diagnosis and reporting capabilities, helping in troubleshooting and ensuring vehicles meet emissions standards.
How to Use the OBD2 Port
Using the OBD2 port is straightforward. Simply plug a compatible scanner into the OBD2 port to communicate with the car's computer system and read faults codes that indicate vehicle issues. If your car was manufactured after 1996, it is required by law to have an OBD2 port.
Take Vehicle Diagnostics to the Next Level
While the standard OBD2 port provides access to basic diagnostic data, such as fault codes, sensor readings, and emissions status, it only scratches the surface of what your vehicle’s internal systems are capable of reporting. For those who require deeper visibility, faster data acquisition, and access to non-emissions-related ECUs, the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro offers a significant upgrade.
The AutoPi CAN-FD Pro builds on the OBD2 interface by enabling access to both traditional CAN and modern CAN FD (Flexible Data-rate) protocols. This means you can capture high-speed, high-resolution data from a broader range of control units, including powertrain, body, chassis, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Whether you're developing telematics solutions, optimizing vehicle performance, or conducting fleet-level diagnostics, this device provides a flexible and scalable platform.
With integrated features like real-time data logging, remote access via the AutoPi Cloud, and support for custom triggers and automation, the CAN-FD Pro transforms the standard OBD2 port into a gateway for advanced diagnostics and system-level monitoring. It’s engineered for professionals and developers who need reliable, low-level access to the vehicle network beyond what a typical OBD2 scanner can offer.
If you're looking to go beyond fault code reading and want full visibility into your vehicle’s behavior, the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro is a purpose-built solution designed to support the next generation of connected automotive applications.

FAQs About OBD2 Port Location and Use
-
What if I can’t find my car’s OBD2 port location?
Start by checking under the dashboard on the driver's side, near the steering column or above the pedals. It may be hidden behind a trim panel. If not visible, consult your owner’s manual or search online using your vehicle’s make, model, and year. You can also refer to our AutoPi OBD2 documentation. -
Are all OBD2 ports and connectors the same across vehicles?
Yes, all OBD2 ports follow the SAE J1962 standard, ensuring a universal 16-pin connector. While the physical connector is always the same, the underlying protocols (CAN, ISO 9141, etc.) may vary between manufacturers. -
How many OBD2 ports does a standard car have?
Most passenger vehicles have only one OBD2 port. This single diagnostic port provides access to emissions, engine, and vehicle health data. Commercial or specialized vehicles may have additional proprietary connectors. -
Is the location of the OBD2 port the same in every car?
No, port locations vary by model and manufacturer. Most are under the dashboard or near the steering wheel, but some are hidden behind covers or integrated into center consoles or fuse box panels. -
Can OBD2 port placement vary by vehicle type?
Yes, in compact cars it's usually low on the driver’s side, while in trucks or EVs it may be in fuse panels, side consoles, or utility compartments. Right-hand drive vehicles may have mirrored placements. -
What does the OBD2 connector look like?
It’s a trapezoidal 16-pin female connector, black or dark gray, with two rows of 8 pins. The shape ensures it fits in only one direction for secure connections with scanners and devices. -
Is it safe to leave a device plugged into the OBD2 port?
Yes, most OBD2 tools are designed for continuous use. However, if your vehicle is parked for long periods, be aware that some devices may draw small amounts of power even when the ignition is off. -
Can I use an OBD2 extension cable to relocate the port?
Absolutely. Extension cables help relocate the port to a more convenient location and protect the original connector from wear and frequent unplugging, ideal for fleet and development setups. -
Do electric vehicles (EVs) have an OBD2 port?
Yes. EVs still include an OBD2 port for diagnostics, although available data differs from combustion engines. You may need manufacturer-specific tools for advanced battery and drivetrain data. -
Can I diagnose engine problems through the OBD2 port?
Yes. The port provides access to diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), live sensor data, and readiness monitors. It's essential for identifying and addressing performance issues or system faults. -
Does every car manufactured after 1996 have an OBD2 port?
In most regions, yes. All gasoline vehicles from 1996 onward (and diesel vehicles from 2004) must include an OBD2 port under emissions compliance regulations such as OBD-II and EOBD. -
What are common problems with OBD2 ports?
Issues include bent pins, debris, loose sockets, or blown fuses on the diagnostic circuit. If a scanner doesn’t respond, check for power at pin 16 and verify ground at pins 4 and 5. -
Can I use the OBD2 port while driving?
Yes, many tools are designed for real-time use while the vehicle is running. This allows live data streaming for engine diagnostics, driving behavior analysis, and GPS tracking via connected devices. -
What tools can I connect to the OBD2 port?
You can use handheld scanners, Bluetooth/WiFi adapters, telematics platforms like the AutoPi TMU CM4, and OEM-grade diagnostic systems. Each offers different levels of data access and functionality.
Conclusion
The vehicle diagnostic port is more than just a plug in your car, it's a portal to understanding your vehicle's health and status. The next time you find yourself with a dashboard warning light, remember the power of the OBD2 port at your fingertips. Embrace the capabilities of the OBD2 port to keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
Explore our range of OBD2 tools and automotive data loggers to keep your vehicle in top condition, and start leveraging the power of advanced diagnostics today!





