Welcome to the dynamic world of telematics in cars, a key area of expertise for us here at Autop
Have you ever wondered how your car collects and utilizes data? That's the magic of telematics—it's the smart tech that blends telecommunications with informatics to boost your car's safety, efficiency, and connectivity.
At AutoPi, telematics isn't just another features; it's at the core of what we do every day. We're passionate about demonstrating how this technology isn't only for high-end cars but is increasingly needed in vehicles of all types, making telematics an essential management tool for many individual drivers and commercial fleets, even government fleets.
Let's get started and explore how telematics works and why it's becoming essential in modern vehicles.
What is Telematics?
Think of telematics as a smart computer right in your car that keeps an eye on almost everything about your drive. It's what turns your vehicle into a smart device, connecting you better to the road and beyond.
Telematics Definition
Telematics combines telecommunications and computer science to collect and send data about your car. This information, or telematics data, is recorded via a small telematics device, also called a black box, that plus into the OBD-II port. It powers useful features like real-time traffic updates, quick help during emergencies, and tailored insurance rates based on how you drive.
This tech isn't just about keeping you safe—it also boosts your car's efficiency. With telematics you're always in the loop about how your car is performing, whether it's fuel efficiency or the best routes to avoid traffic. It can even spot potential problems before they leave you stranded. It's how Tesla get data from their cars.
As this technology gets even smart, it's paving the way for cars that are more automated and connected. While there is no fully automated vehicles for sales right now, however, one thing is clear, we're only getting closer to a level 5 automation.

How Does Telematics Work?
Telematics rely on a combination of advanced hardware and smart software. This combination is the driving force behind the telematics systems, making modern vehicles smarter and more efficient. Let’s break down how it all works:
Telematics Hardware Components
The hardware in a telematics system is essential for gathering and sending data. Key parts include:
-
Telematics Control Unit (TCU): The central unit that connects various sensors and communication modules.
-
GPS Module: Tracks the vehicle's real-time location.
-
Onboard Diagnostics (OBD-II) Port: Monitors engine health and performance by tapping into the car's internal diagnostics system.
Sensors: Collect information on speed, braking, and other driving behaviors.
-
Cellular Modem: Sends data securely and in real-time over cellular network.
Telematics Software Components
The software processes and analyzes the data collected by the hardware. This includes:
-
Data Processing Algorithms: Turn raw data into useful insights, like maintenance alerts.
-
Machine Learning Models: Predict potential problems before they happen, helping with preventive maintenance.
-
User Interface (UI): Lets drivers and fleet managers view and interact with the data through dashboards, apps, or websites.
Data Collection
After collecting the data, the system sends it from the vehicle to the central server via the cellular modem. This ensures the data is sent securely and in real-time. For example, if a vehicle's engine starts to overheat, the system can immediately alert the driver and the maintenance team.
Data Processing and Analysis
On the server, the data is processed and analyzed. Advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques help turn this data into actionable insights. For instance:
-
GPS Tracking: Provides real-time navigation and traffic updates.
-
Vehicle Diagnostics: Generates alerts for needed maintenance, preventing breakdowns.
-
Driver Behavior: Offers tips to improve driving habits and enhance safety.
Practical Applications
The processed data is then used to improve the vehicle's functionality and the driver's experience in several ways:
-
Automated Emergency Services: In an accidents, the system can automatically send the vehicle's location and crash details to emergency services, speeding up response times.
-
Vehicle Diagnostics and Maintenance: Regular health updates help schedule timely maintenance, extending the vehicle's lifespan and ensuring safety.
-
Driver Assistance: Real-time traffic data helps optimize routes, saving time and fuel.
Example: GPS Tracking
Imagine a GPS tracking system in a telematics-enabled vehicle. As the vehicle moves, the GPS module logs its location every second. This data is sent via cellular networks to a central server, where it's processed and made available in real-time on a mobile app. This helps with navigation and locating the vehicle if it's stolen.
Example: Automated Emergency Services
If there's a collision, sensors in the vehicle detect the impact and trigger an alert. The telematics system sends critical details, like the vehicle's exact location and crash severity, to emergency responders. This quick communication can significantly reduce response times, potentially saving lives.
History of Telematics
The story of telematics is one of remarkable technological progress, combining telecommunication and informatics to revolutionize vehicle technology.
Early Beginnings
-
1960s-1970s: It all started in the military and aerospace sectors for navigation and tracking, using early telecommunication and informatics technologies.
-
1980s: Telematics moved into civilian use, especially in fleet management with basic GPS tracking.
The Rise of GPS and Cellular Networks
-
1990s: GPS became commercial, and better cellular networks allowed real-time data transmission. This powerful mix of telecommunication (GPS and cellular networks) and informatics (data processing) expanded what telematics could do.
-
1996: The U.S. government made GPS available for everyone, boosting the use of telematics.
Integration with Automotive Technology
-
Early 2000s: Car makers started adding telematics for navigation and emergency help, integrating telecommunications and informatics more deeply into vehicles.
-
Mid-2000s: Telematics began using onboard diagnostics (OBD) for real-time vehicle health checks.
Modern Developments
-
2010s-Present: Now, telematics uses IoT, machine learning, and big data for advanced features like driver behavior insights and predictive maintenance.
-
Electric and Autonomous Vehicles: It plays a crucial role in the growth of electric vehicles and self-driving cars, enhancing safety and efficiency.
By combining telecommunication and informatics, telematics has evolved from military roots to a key technology in modern vehicles. This combination drives innovation and shapes the future of travel.
Stay Ahead with AutoPi: The Next Step in Telematics
Telematics has come a long way, hasn’t it? It's wild how much things have changed. Here at AutoPi, we're really excited to be part of it all. Connecting your fleet to smart tech isn’t just a nice-to-have anymore—it’s really important for businesses who want to save time, cut costs, and stay on top of safety.
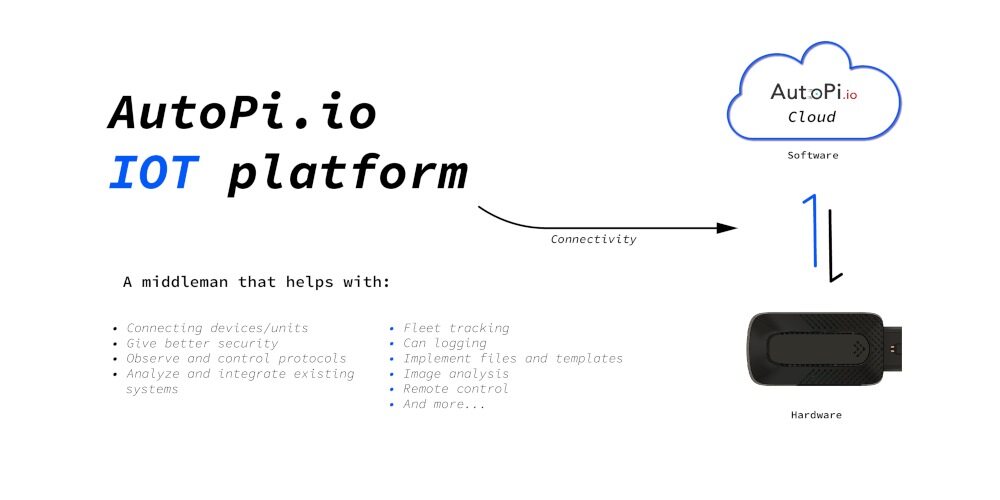
That’s where AutoPi comes in. We’ve got a few devices that can make all of this much easier for you.
AutoPi Can FD Pro, TMU CM4, and Mini Devices
AutoPi Can FD Pro: If you’re running a business that needs detailed vehicle data, the AutoPi Can FD Pro is the one. It tracks everything from fuel efficiency to engine health, helping you avoid surprises and keep things running smoothly. Perfect for companies that need more in-depth insights into their vehicles.


AutoPi TMU CM4: For fleet managers, the AutoPi TMU CM4 is a real game changer. It tracks your drivers, your vehicles, and your routes, giving you data to help save on fuel, predict maintenance, and keep your fleet running like a well-oiled machine.
AutoPi Mini: If you just need something simple, the AutoPi Mini is your best bet. It’s small, easy to install, and covers the basics—GPS tracking and vehicle health. It’s perfect for smaller fleets or businesses just starting to explore telematics.

Pros and Cons of Telematics
Telematics have a lot to offer but come with some challenges too. Here's a look at the pros and cons, including for fleet telematics.
|
Aspect
|
Pros
|
Cons
|
|---|---|---|
| Safety |
- Real-time alerts for quick action
- Automatic emergency response |
- |
| Efficiency |
- Fuel management to reduce costs
- Maintenance alerts to prevent breakdowns |
- |
| Driver Behavior Monitoring |
- Tracks and analyzes driving habits
- Provides feedback and incentives for safer driving |
- Privacy concerns with data collection
- Potential driver discomfort |
| Cost Savings |
- Reduces fuel and maintenance costs
- Insurance benefits from lower premiums |
- High initial setup costs
- Ongoing subscription fees |
| Privacy and Security | - Introduced blockchain that can enhance data security and transparency |
- Constant monitoring can feel intrusive
- Data security risks require strong protection measures |
| Complexity and Maintenance | - |
- System integration can be complex
- Regular maintenance and updates are necessary |
| Driver Dependency | - | - Risk of drivers becoming too reliant on telematics systems, potentially reducing driving skills |
After examining the pros and cons, you can see how each aspect balances out. To make a well-informed decision, consider assigning weights or scores to each pro and con. This can help you calculate the net value of each option.
Ultimately, choose the option that has the most pros and the fewest cons, while also aligning best with your goals, values, and preferences. This approach ensures that you select a telematics system that meets your needs effectively and supports your objectives.
Fleet Telematics
When it comes to fleet telematics, the benefits and challenges are quite specific. Here's a closer look at the pros and cons of fleet telematics:
|
Aspect
|
Fleet Telematics Pros
|
Fleet Telematics Cons
|
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency |
- Better route planning
- Enhanced operational efficiency |
- Managing and analyzing large volumes of data can be overwhelming |
| Safety |
- Improved driver behavior monitoring
- Real-time alerts |
- |
| Cost Savings | - Lower operational costs | - |
| Driver Resistance | - | - Some drivers might resist using telematics, feeling it invades their privacy or adds pressure |
While fleet telematics can greatly enhance efficiency, safety, and cost savings, it’s important to be aware of the potential challenges, such as data management and driver resistance. Weighing these pros and cons can help fleet managers make informed decisions about implementing telematics in their operations.
Ultimately, the benefits of fleet telematics often outweigh the drawbacks, especially when managed effectively and aligned with organizational goals and values.
Telematics Devices
Telematics devices are the heart of any telematics system, helping to gather, send, and analyze vehicle data. Let's look at the different types of telematics devices and how they work in modern vehicles.
Types of Telematics Devices
1. GPS Trackers
GPS trackers are the simplest type of telematics device. They use GPS technology to provide real-time location data for vehicles.
-
Function: Track where the vehicle is, its speed, and its route history.
-
Benefits: Great for navigation, recovering stolen vehicles, and planning routes.
2. Onboard Diagnostics (OBD-II) Devices
OBD-II devices plug into the vehicle's diagnostics port. They collect data on how the vehicle is performing and its health.
-
Function: Monitor engine performance, fuel efficiency, and other diagnostics.
-
Benefits: Useful for getting maintenance alerts, managing fuel use, and keeping the vehicle in good health.
3. Telematics Control Units (TCUs)
Telematics Control Units are advanced devices that combine several functions, including GPS tracking, diagnostics, and communication.
-
Function: Gather and send data from various sensors in the vehicle to a central server.
-
Benefits: Provide comprehensive data collection and real-time communication for better vehicle management.
4. Dash Cameras
Dash cameras are often used with telematics systems to provide visual data that supports other sensor data.
-
Function: Record video of the road and driver behavior.
-
Benefits: Useful for investigating accidents, training drivers, and improving safety.
5. Fleet Management Systems
These systems are designed for managing large fleets of vehicles. They integrate multiple telematics devices to provide a centralized platform for data management.
-
Function: Combine GPS tracking, diagnostics, and driver behavior monitoring.
-
Benefits: Streamline fleet operations, improve efficiency, and ensure compliance with regulations.
Importance of Telematics Devices
Telematics devices are crucial for a fully integrated telematics system. They constantly gather and send data, which is then processed and analyzed to provide useful insights. Here’s why they are important:
-
Real-time Data Collection: They provide real-time data on vehicle location, performance, and driver behavior, allowing for quick decisions and timely actions.
-
Enhanced Safety: Devices like GPS trackers and dash cameras enhance safety by offering real-time alerts and visual records of incidents.
-
Improved Efficiency: OBD-II devices and TCUs help monitor and optimize vehicle performance, reducing fuel use and maintenance costs.
-
Compliance and Reporting: Fleet management systems help meet regulatory requirements by keeping detailed logs of vehicle use and driver behavior.
Telematics devices form the backbone of telematics systems, making modern vehicles smarter, safer, and more efficient. Knowing about the different types of devices and their roles can help you choose the right telematics solutions for your needs.
Integration of Telematics in Modern Vehicles
Telematics technology is becoming a standard feature in modern vehicles, seamlessly integrating with various in-car systems to enhance the driving experience. Here’s how telematics is being integrated into today’s cars and the benefits it brings.
Seamless Integration with In-Car Systems
Infotainment Systems
Modern cars come with advanced infotainment systems that include GPS navigation, multimedia features, and internet connectivity. Telematics makes these systems even better by providing real-time traffic updates, location-based services, and emergency help.
-
Example: Real-time traffic updates help drivers avoid congested routes, saving time and fuel.
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Telematics works with ADAS to improve safety features like collision avoidance, lane departure warnings, and adaptive cruise control. The data from telematics helps these systems make smarter decisions, enhancing overall vehicle safety.
-
Example: Lane departure warnings use telematics data to alert drivers when they unintentionally drift out of their lane.
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Telematics is crucial for electric vehicles by monitoring battery health, managing charging, and optimizing energy use. It also helps EV owners find nearby charging stations and plan longer trips more effectively.
-
Example: Telematics systems can provide real-time information on the nearest charging stations and their availability.
Benefits of Integration
Enhanced Connectivity
Telematics systems enable vehicles to connect with each other and with infrastructure (Vehicle-to-Everything or V2X). This connectivity allows for smoother traffic flow, better road safety, and more efficient vehicle management.
-
Example: Vehicles communicating with traffic lights to reduce idle time and improve fuel efficiency.
Data-Driven Insights
The integration of telematics provides valuable data that can be used to improve vehicle performance, enhance safety features, and offer personalized driving experiences. Manufacturers can use this data to innovate and develop better vehicles.
-
Example: Personalized driving tips based on individual driving habits to improve fuel efficiency and safety.
Support for Autonomous Driving
Telematics is a key component in the development of autonomous vehicles. By providing real-time data and communication capabilities, telematics helps autonomous vehicles navigate and make decisions safely.
-
Example: Autonomous cars using telematics to detect obstacles and navigate through traffic safely.
Fleet Management
For businesses, the integration of telematics in fleet vehicles offers significant benefits, including improved route planning, real-time vehicle tracking, and better driver management. This leads to increased efficiency and reduced operational costs.
-
Example: Fleet managers using telematics to monitor vehicle locations and optimize delivery routes.
Future Trends
As technology continues to advance, the integration of telematics in vehicles is expected to grow even more sophisticated. Future trends include:
-
Greater Use of AI and Machine Learning: Enhancing predictive maintenance and personalized driving experiences.
-
Increased Connectivity: Expansion of V2X communication for smarter city infrastructure and improved traffic management.
-
Enhanced Security Measures: Improving data protection and privacy for telematics systems.
The seamless integration of telematics in modern vehicles is transforming the automotive industry, making driving safer, more efficient, and more enjoyable. As telematics technology continues to evolve, its role in our daily driving experiences will only become more significant.
Conclusion
Telematics has changed the way we manage our vehicles. It provides real-time data, boosts safety, and improves efficiency. From GPS trackers to advanced fleet systems, telematics makes cars smarter and more connected.
Telematics offers many benefits, like better fuel management and safer driving. But it also has challenges, such as data privacy and high setup costs. Knowing these pros and cons helps you make smart decisions about using telematics.
The future of telematics is exciting with new advancements in AI and connectivity. Whether you're a car owner or manage a fleet, telematics can help you optimize your driving and operations.
Ready to see how telematics can help you? Contact us today to learn more about our telematics solutions. Get in touch with us now.







