Diagnostic over Internet Protocol (DoIP) is an automotive diagnostics transport that carries diagnostic messages over IP networks. In practice, it is the mechanism that allows common diagnostic services (for example UDS routines, trouble code readout, ECU identification, and flashing workflows) to run over Ethernet instead of slower legacy links.
DoIP is most relevant in vehicles with an in-vehicle Ethernet backbone, where high data throughput is needed for diagnostics and ECU programming. As ECUs have grown in number and firmware images have increased in size, traditional point-to-point diagnostic transports such as K-Line, and even CAN-based diagnostics, become an obvious constraint in workshop and production environments. DoIP moves the transport to IP and shifts the bottleneck toward network design, gateway behavior, and access control.
From an engineering perspective, DoIP is not “a new set of diagnostic services”. The diagnostic services remain familiar (UDS is still UDS). The change is how diagnostic traffic is transported, routed, and session-managed. This is why DoIP often shows up together with ISO 14229 (UDS) and OEM-specific security layers, while ISO 13400 defines the DoIP framing, discovery, and routing activation behavior.
DoIP is also a response to modern software-defined vehicles and the practical need to run larger diagnostic sessions reliably. Firmware flashing, measuring blocks, DTC snapshots, and ECU variant coding can generate traffic volumes where older transports are simply slow. Ethernet-based transport reduces flashing time, reduces diagnostic session duration, and makes large readouts more predictable, assuming the gateway and network remain stable during the session.
At AutoPi, DoIP is treated as a production-grade requirement rather than a lab protocol. The team has spent years working with vehicle communication stacks, embedded Linux systems, and real-world fleet hardware where corner cases appear quickly: routing activation timeouts, gateway resets during flashing, mixed CAN + Ethernet architectures, and OEM differences in how DoIP is exposed. This background matters because ISO compliance alone does not guarantee that a system is practical on real vehicles.
DoIP knowledge is now relevant across vehicle development, validation, aftersales tooling, and fleet operations. Ethernet backbones and DoIP gateways are common in platforms produced in the late 2010s and onward, particularly where ADAS, infotainment, EV power electronics, and domain controllers drive higher data demands.
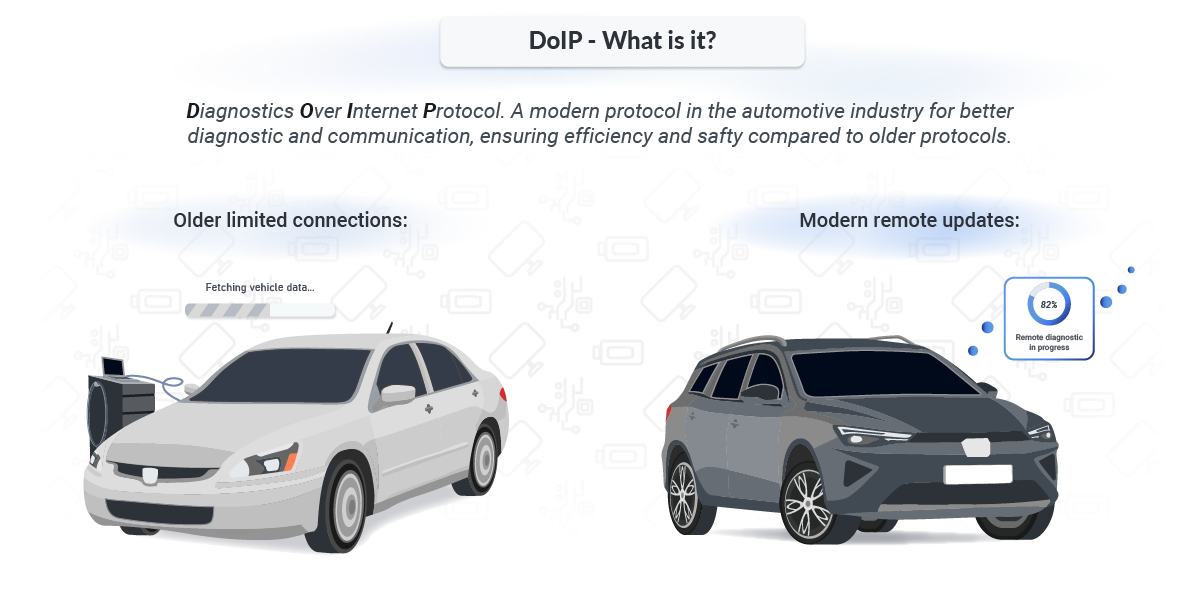
What is DoIP?
DoIP, short for Diagnostic over Internet Protocol, is a diagnostic transport standardized under ISO 13400. It defines how diagnostic communication is packaged and transferred over IP networks, typically Ethernet inside the vehicle. The payload often contains UDS requests and responses (ISO 14229), but DoIP itself covers discovery, session setup, message framing, and routing activation rather than the diagnostic service semantics.
Earlier diagnostic setups depended on direct physical access and point-to-point links. Many systems still support CAN-based diagnostics, and in some platforms CAN remains the only diagnostic path to certain ECUs. DoIP does not invalidate those networks. Instead, it introduces an IP-based entry point that can reach multiple internal networks through a DoIP gateway. That gateway is commonly responsible for bridging from Ethernet to CAN, LIN, FlexRay, or internal diagnostic buses.
A typical DoIP setup includes a DoIP gateway (or a domain controller with gateway functionality), multiple ECUs on internal networks, and an external diagnostic client. The client can be a workshop tester, a production tester, or a telematics unit with controlled diagnostic access. Once routing is activated, diagnostic messages can be addressed to logical targets without relying on a physical diagnostic cable for each ECU.
The protocol became relevant as OEMs introduced in-vehicle Ethernet backbones. Ethernet variants such as 100BASE-T1 and 1000BASE-T1 enable a different class of data transfer than traditional diagnostic transports. This is a key reason DoIP is often discussed in the context of ECU programming, ADAS validation, and high-volume data extraction, where throughput and stability matter more than raw simplicity.
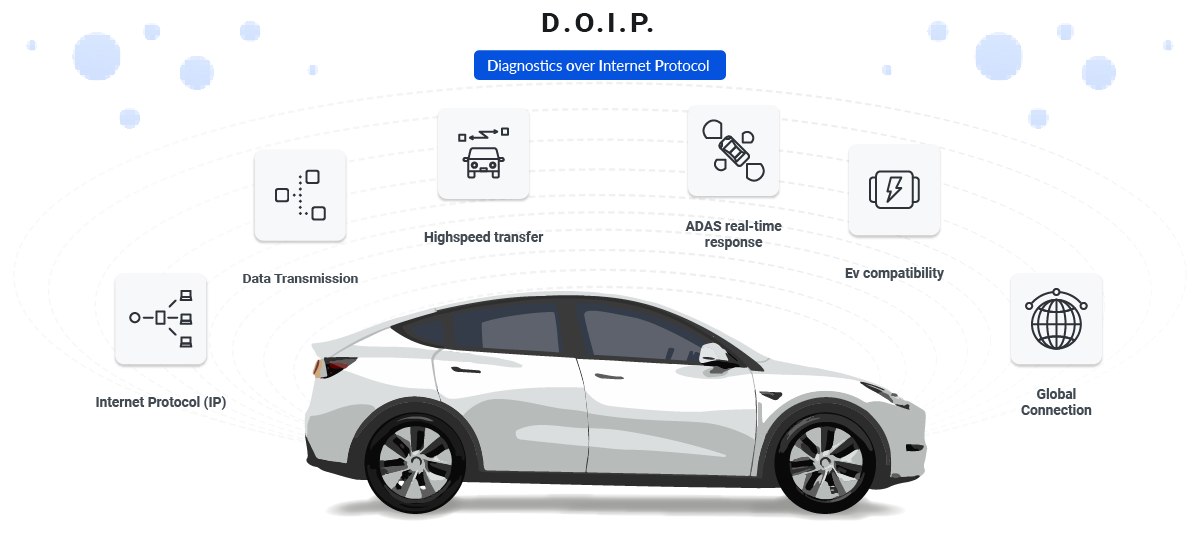
Technical Specifications of DoIP
-
Protocol basis: DoIP uses IP networking (most commonly Ethernet) as the underlying transport. This makes diagnostic communication routable and compatible with standard networking concepts such as addressing, switching, and segmentation.
-
ISO standard: DoIP is standardized under ISO 13400. The standard defines discovery, message framing, routing activation, and how diagnostic payloads are carried over TCP and UDP.
-
Transport behavior: TCP is typically used for diagnostic message exchange where ordered delivery is required (for example ECU programming). UDP is commonly used for discovery and certain control paths.
-
Addressing model: DoIP introduces logical addressing concepts so a diagnostic client can address a specific ECU (or functional group) even when the ECU is not directly reachable on Ethernet.
DoIP represents a structural shift in how diagnostics are accessed and operated. With Ethernet in the vehicle, diagnostic traffic can share infrastructure with other in-vehicle communication, but this also introduces stricter requirements on segmentation, access control, and gateway configuration.
-
ADAS: ADAS ECUs and sensor systems can require more frequent software updates and data extraction. Diagnostics over Ethernet reduces time spent on readouts and programming cycles.
-
Electric vehicles: Battery management, inverter control, and thermal systems often involve dense diagnostics and calibration. High throughput helps, but stability and correct session handling matter just as much.
-
Global operations: DoIP supports remote diagnostics when combined with controlled network access, allowing engineering teams to interact with vehicles without physical presence, subject to OEM policies and security constraints.
The AutoPi CANFD Pro is designed to support DoIP workflows where Ethernet-based diagnostics and vehicle data access are required in engineering and operational environments.
Applications of DoIP in Automotive Technology
In modern vehicle development and service operations, DoIP influences the practical workflow more than most engineers expect initially. It changes how diagnostic sessions are established, how fast data can be moved, and how programming and validation cycles are executed across ECUs that sit behind a gateway.
DoIP also fits naturally into environments where Ethernet is already present for production, end-of-line testing, or prototype validation. A stable network and a predictable gateway configuration often matter more than the headline bandwidth, especially during ECU flashing where retries and timeouts carry a real cost.
Use cases commonly associated with DoIP include:
-
Remote diagnostics: Diagnostic sessions can be executed across a network when access is controlled. This reduces reliance on physical access and allows distributed engineering or support teams to perform readouts and checks.
-
Software updates: Vehicles can receive software updates over-the-air when a platform supports OTA workflows. DoIP is often the transport for diagnostic flashing services in these systems, but OEM security layers and policies still define what is permitted.
-
Manufacturing and quality control: DoIP supports higher throughput during programming and validation on the assembly line. This can reduce station time and simplify certain test setups, but it can also expose network design weaknesses quickly if segmentation and routing rules are not consistent.
Benefits of DoIP
-
Higher throughput in practice: Ethernet transport enables shorter diagnostic cycles, particularly for large ECU programming sessions. The gain is most visible when flashing or extracting logs and datasets.
-
Scalable topology: IP-based diagnostics fit both workshop tools and larger setups such as production plants or fleets. The same base protocol applies, while access control and policy differ.
-
Less dependency on physical handling: Reducing cable swaps and repeated physical access can lower the operational overhead, especially in prototype fleets where vehicles move between teams and sites.
DoIP is rarely “plug and play” across brands. OEM choices around gateway policy, routing activation behavior, firewalling, and security access can heavily influence practical usability. That is why implementation details, logging, and visibility into sessions matter.
Challenges and Solutions
-
Network security: Network-based diagnostics increase the importance of access control. A DoIP gateway is an entry point into diagnostic functions that can alter ECU behavior.
-
Solution: Enforce routing activation rules, apply strict authentication, and use encryption mechanisms where the broader platform supports it. In practice, this is often implemented as a combination of OEM security access, gateway policy, and backend authorization.
-
-
Integration with existing systems: Mixed vehicle architectures are common. Some ECUs are reachable through DoIP, while others remain only reachable over CAN or LIN behind the gateway.
-
Solution: Use bridging and middleware that can manage both DoIP sessions and legacy buses, while keeping addressing and session state consistent across transports.
-
-
Operational stability: Flashing sessions can fail due to gateway resets, link instability, or timing issues in the session control layer.
-
Solution: Add session observability and controlled retries, and treat DoIP as a network service that needs monitoring (latency, packet loss, reconnect behavior), not only a diagnostic protocol.
-
Addressing these challenges is less about adding “more protocol” and more about engineering predictable access and repeatable behavior. That includes stable routing activation, clear separation of roles, and a realistic view of how OEM security impacts diagnostic access.
A practical example from AutoPi environments is the use of DoIP together with remote update workflows, where controlled access to diagnostic sessions reduces the operational burden of physically recalling vehicles. The measurable outcome depends on the vehicle platform and update scope, but the main engineering win is repeatability: a known session flow, traceable logs, and fewer manual interventions.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Background |
Industry: Transportation and Logistics Fleet size: 300+ vehicles (example deployment profile) Goal: Reduce operational overhead and shorten update cycles for distributed vehicles. |
| Implementation |
Remote diagnostics: Diagnostic sessions executed over IP with controlled access. Automated software updates: OTA workflow using OTA updates to coordinate update delivery and reduce manual handling. |
| Observed effects |
Shorter diagnostic sessions: Faster readouts and programming flows compared to legacy-only transports. Lower operational load: Fewer physical service actions for update campaigns. Improved traceability: Better logging and repeatability during maintenance windows. |
"DoIP is most useful when it is treated as a reliable network service with good visibility, not just a faster cable replacement. Stable routing activation, predictable session handling, and trace logs make the difference during flashing and remote workflows."

Technical Overview of DoIP
DoIP is often described as “diagnostics over Ethernet”, but the practical implementation has several moving parts: discovery, session establishment, routing activation, logical addressing, and the actual diagnostic payload exchange. This is why a DoIP trace typically contains both control-plane traffic and diagnostic payload traffic.
DoIP sessions commonly begin with discovery and identification, followed by routing activation, and only then the diagnostic message stream. In real vehicles, the gateway behavior varies between brands and sometimes between model years. Small differences in timing, gateway policy, and security access routines can decide whether a session is stable.

Core Technical Aspects of DoIP
Protocol Basics:
-
Foundation: DoIP is defined by ISO 13400. It specifies discovery behavior, message framing, and the routing activation step used to open a diagnostic route through the gateway.
-
Transport layer: Diagnostic payload exchange typically uses TCP/IP. UDP/IP is commonly used for discovery and certain control messages. Practical tooling often inspects both TCP and UDP flows.
Network Configuration:
-
Vehicle identification: VIN is commonly used in identification steps and in diagnostics metadata, but real discovery flows also depend on gateway configuration and addressing rules.
-
Gateway functionality: The DoIP gateway routes diagnostic traffic between the IP network and internal vehicle networks. In many architectures it also enforces policy: which logical targets are reachable, when, and under what activation rules.
Session Control:
-
Diagnostic session initiation: DoIP sessions are started through network discovery and activation, rather than requiring a dedicated physical link to each ECU.
-
Routing activation: The routing activation step establishes the permitted path for diagnostic exchange. OEMs can implement additional constraints around this step, including authentication and session limits.
Data Handling and Security:
-
Encryption and authentication: Security is often implemented as part of the broader vehicle platform rather than purely within DoIP. This can include OEM security access routines, backend authorization, and network segmentation.
-
Diagnostic message format: DoIP uses standardized framing and payload types, allowing diagnostic clients to handle message routing and decoding in a consistent way.
Performance and Scalability:
-
High-speed data transfer: DoIP supports higher throughput than traditional diagnostic transports, which is most visible during ECU flashing and large dataset extraction.
-
Scalability: The protocol adapts to single-vehicle workshop usage and to multi-vehicle environments such as production lines or distributed test fleets, assuming access control is engineered correctly.
Advantages of Technical Implementation
DoIP’s technical characteristics make it a practical fit for modern diagnostic workflows, but the real benefit comes when network stability, gateway policy, and session observability are handled properly.
-
Efficiency: Faster diagnostic and programming cycles reduce the time needed for controlled service and validation tasks.
-
Flexibility: IP transport allows integration with Linux-based tooling and test setups, including packet capture and automated regression testing of diagnostic flows.
-
Cost control: Fewer manual interventions and less physical handling can reduce operational effort over time, particularly in fleets and prototype programs.
DoIP vs. Traditional Protocols
DoIP changes the constraints of vehicle diagnostics. With CAN-based diagnostics, bandwidth and bus load become the obvious limit. With DoIP, the limiting factor is often gateway policy, network segmentation, and the stability of the IP path during long programming sessions.
Traditional diagnostic protocols such as K-Line and CAN-based diagnostics remain relevant, and many vehicles still require those paths for certain ECUs or for fallback operation. DoIP is not a replacement for CAN as an in-vehicle control network. It is a transport for diagnostics that aligns with Ethernet-based architectures and high data volume requirements.
| Feature | DoIP | Traditional Protocols |
|---|---|---|
| Network Integration | Operates over IP networks (commonly Ethernet), enabling routed diagnostics and controlled remote access. | Relies on point-to-point or bus-based connections like CAN or K-Line. |
| Data Transfer Speed | Supports higher throughput, useful for ECU flashing and large diagnostic reads. | Limited by lower data rates, often increasing session time for large operations. |
| System Compatibility | Aligns with Ethernet-based vehicle architectures and domain controller designs. | May require bridging when vehicle architecture shifts toward Ethernet backbones. |
| Scalability | Scales from workshop usage to production and fleet environments, with policy-driven access control. | Scaling often depends on additional hardware and manual handling. |
| Operational Cost | Can reduce physical handling and repeat service actions when engineered with proper access control. | Higher ongoing overhead when processes require repeated physical access and manual intervention. |
DoIP supports the current direction of vehicle architectures, but the practical outcome depends on gateway policy, security access constraints, and how diagnostic sessions are monitored and controlled.
AutoPi DoIP Solution: Vehicle Diagnostics and ECU Programming Workflows
AutoPi devices support DoIP-based workflows as part of a wider hardware and software platform used for vehicle data access, diagnostics, and update operations. A typical setup combines DoIP over Ethernet with Linux-based tooling, allowing diagnostic sessions to be logged, reproduced, and integrated into engineering processes rather than handled as a one-off workshop action.
DoIP capability is commonly paired with features such as real-time data streaming and controlled update flows via OTA updates. The intent is predictable behavior: controlled access, traceable sessions, and diagnostic workflows that can be repeated across fleets and prototype programs.
-
DoIP is relevant when diagnostic data volume and programming workflows exceed what legacy transports handle efficiently.
-
Ethernet-based diagnostics support faster diagnostic sessions and ECU flashing, assuming stable routing activation and correct gateway policy.
-
DoIP is standardized under ISO 13400 and is commonly used together with UDS services for practical diagnostic operations.
-
Vehicle platform differences matter. Real-world DoIP behavior can vary by OEM, model year, and gateway configuration, so practical implementations need traceability and clear session handling.
For further details on DoIP capabilities and integration references:
-
Visit the documentation page.
-
Integration discussions and technical requirements can be handled through sales inquiry.





