DoIP is a modern protocol used in the automotive industry for diagnostics and communication between vehicle components and external diagnostic equipment. This technology plays a crucial role in diagnosing and maintaining vehicles, ensuring they operate efficiently and safely.
As vehicles become more connected and complex, the need for advanced diagnostic capabilities increases. DoIP provides a robust framework that allows for faster, more reliable data transmission compared to older protocols.
This means quicker diagnostics, more accurate fault detection, and the ability to manage modern vehicle technologies more effectively.
At AutoPi, we've dedicated over two decades combined to mastering automotive diagnostics and communication technologies. Our expertise in DoIP stems from years of developing solutions that harness the power of this protocol to enhance vehicle performance and safety.
Whether you're a vehicle manufacturer, a service provider, or a technology enthusiast, understanding DoIP will help you appreciate how it transforms automotive diagnostics.
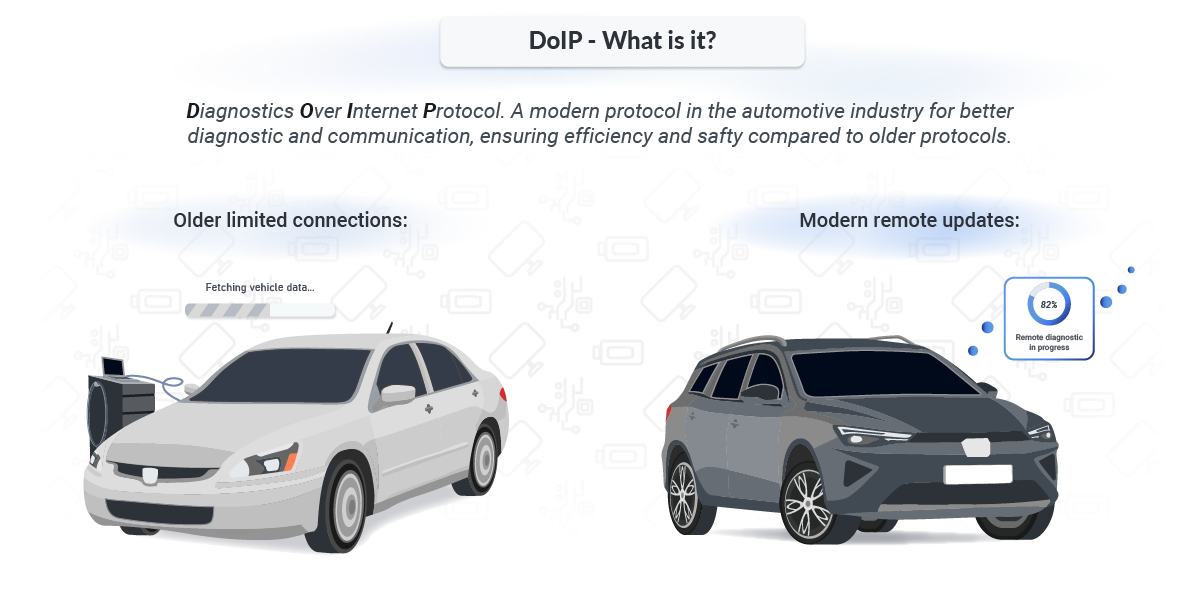
What is DoIP?
DoIP, or Diagnostic over Internet Protocol, is a protocol used for vehicle diagnostics (DTC codes) that operates over IP networks.
Unlike traditional diagnostic systems that relied on direct physical connections, DoIP facilitates communication over a network, allowing remote diagnostics and updates. This ability is crucial in modern vehicles that integrate advanced electronics and require frequent software updates.
The concept of DoIP emerged from the need for more efficient diagnostic methods as vehicles evolved. Previously, vehicle diagnostics were limited by the speed and range of the connections available. With the advent of the Internet and network technologies,
DoIP was developed to leverage these broader, faster networks, enhancing the scope and efficiency of diagnostics.
Technical Specifications of DoIP
-
Protocol Basis: DoIP uses the Internet Protocol (IP) as its basis, ensuring it can operate over any network that supports IP, including Ethernet.
-
ISO Standard: It is standardized under ISO 13400, which dictates how data is transmitted and secured across networks.
-
Data Transfer: Allows for high-speed data transfer between diagnostic tools and vehicle systems, supporting faster updates and more comprehensive diagnostics.
DoIP is more than just a technical upgrade; it represents a shift towards more interconnected and remotely accessible vehicle systems. This shift is vital for supporting:
-
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS): Faster diagnostics and updates for complex systems that require real-time data.
-
Electric Vehicles (EVs): Efficient management of software that controls battery management systems and other critical functions.
-
Global Operations: Enables manufacturers and service providers to perform diagnostics and updates without being physically present, reducing downtime and operational costs.
The AutoPi CANFD Pro is a powerful tool that leverages DoIP to enhance vehicle diagnostics and updates, making it ideal for modern automotive applications.
Applications of DoIP in Automotive Technology
In the rapidly evolving landscape of automotive technology, the integration of DoIP is reshaping how vehicles are serviced and maintained.
This advanced protocol enhances traditional practices and ushers in a new era of diagnostic capabilities.
With DoIP, real-time troubleshooting and streamlined updates are no longer confined to the workshop; they can be performed remotely, creating a seamless and efficient process that benefits manufacturers, technicians, and vehicle owners alike.
Here's some examples of use cases of DoIP in automotives.
-
Remote Diagnostics: Technicians can now diagnose issues from a distance, minimizing the need for in-person service appointments and reducing vehicle downtime.
-
Software Updates: Vehicles can receive the latest software updates over-the-air, ensuring they are always equipped with the newest features and improvements without the need for a physical service visit.
-
Manufacturing and Quality Control: DoIP's capabilities extend into the manufacturing process, allowing for real-time diagnostics and updates during assembly. This ensures that vehicles meet stringent quality standards with reduced errors and corrections post-production.
Benefits of DoIP
-
Enhanced Efficiency: DoIP's ability to operate over high-speed networks drastically reduces the time required for diagnostics and updates.
-
Scalability: The protocol's network-based nature makes it adaptable to both small workshops and large-scale manufacturing environments.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: By reducing the reliance on physical tools and manual interventions, DoIP cuts operational costs and enhances service quality.
The strategic adoption of DoIP not only optimizes operational workflows but also serves as a cornerstone for future advancements in vehicle technology. By aligning with modern communication standards, DoIP sets a new benchmark in automotive diagnostics and maintenance.
Challenges and Solutions
-
Network Security: The shift to network-based diagnostics introduces significant data security challenges.
-
Solution: Implementing state-of-the-art cybersecurity measures, including encryption and secure authentication protocols, ensures that diagnostic data remains protected.
-
Integration with Existing Systems: Many older vehicles and systems use different standards, which can complicate the integration of DoIP.
-
Solution: Creating adaptable interfaces and middleware solutions enables DoIP to communicate effectively across diverse systems, mitigating integration issues.
In addressing these challenges, DoIP not only improves its applicability and security but also ensures a smoother transition for all stakeholders involved. This proactive approach to overcoming obstacles underscores the robustness and adaptability of DoIP in modern automotive systems.
Now, let's see this use case from our company, showing how we've successfully implemented DoIP to enhance their fleet management system.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Background |
Industry: Transportation and Logistics Fleet Size: Over 300 Vehicles Challenge: Reduce downtime and improve efficiency of software updates. |
| Implementation |
Remote Diagnostics: Enabled remote diagnostics to reduce physical checks. Automated Software Updates: Introduced OTA updates for simultaneous software improvements. |
| Results |
Reduced Downtime: Cut vehicle downtime by 40% through quicker issue resolution. Cost Savings: Decreased costs associated with manual updates and maintenance. Improved Fleet Performance: Enhanced reliability and reduced breakdowns through continuous monitoring. |
Technical Overview of DoIP
DoIP is an innovative protocol designed to meet the sophisticated needs of modern automotive diagnostics.
Utilizing the robust infrastructure of Internet Protocol networks, DoIP enables efficient communication between vehicles and diagnostic equipment, regardless of the physical location.

Core Technical Aspects of DoIP
Protocol Basics:
-
Foundation: DoIP operates on the ISO 13400 standard, which specifies how diagnostic communication over Ethernet (DoIP) should be structured.
-
Transport Layer: Utilizes TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) or UDP/IP (User Datagram Protocol/Internet Protocol) for data transmission, ensuring reliable and efficient data exchange.
Network Configuration:
-
Vehicle Identification: Each vehicle is identified on the network through a unique Vehicle Identification Number (VIN), which is transmitted at the beginning of every DoIP session.
-
Gateway Functionality: Acts as a gateway in the vehicle’s network, routing diagnostic messages between external test equipment and the vehicle’s internal network nodes.
Session Control:
-
Diagnostic Session Initiation: DoIP allows for the initiation of diagnostic sessions without physical connections, using just the network capabilities.
-
Routing Activation: Ensures secure communication by establishing a specific route for data exchange, protecting against unauthorized access.
Data Handling and Security:
-
Encryption and Authentication: Employs robust security protocols to safeguard data transmission, preventing interception or manipulation.
-
Diagnostic Message Format: Uses a standardized message format, which includes the VIN, source address, and target address, enhancing clarity and accuracy in diagnostics.
Performance and Scalability:
-
High-Speed Data Transfer: Capable of handling high volumes of data at greater speeds compared to traditional protocols, significantly improving diagnostic times and system updates.
-
Scalability: Easily adapts to different network sizes, from individual vehicles to entire fleets, without necessitating significant changes in infrastructure.
Advantages of Technical Implementation
DoIP's technical attributes contribute significantly to its effectiveness in automotive diagnostics:
-
Efficiency: Reduces the time required for diagnostics and software updates, allowing for faster turnaround times in maintenance and repair.
-
Flexibility: Can be implemented in various settings, from small repair shops to large manufacturing plants, with minimal adjustments.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Decreases the need for extensive hardware setups and reduces operational costs over time due to its network-based nature.
By leveraging the power of IP networks, DoIP not only enhances the capability and efficiency of vehicle diagnostics but also ensures greater security and adaptability for future technological advancements.
DoIP vs. Traditional Protocols
Now let's explore how DoIP contrasts with traditional diagnostic protocols. This comparison highlights DoIP's advanced capabilities and practical advantages, illustrating its superiority in addressing the evolving needs of modern automotive diagnostics.
| Feature | DoIP | Traditional Protocols |
|---|---|---|
| Network Integration | Utilizes IP networks, enabling diagnostics and updates over Ethernet or Wi-Fi. | Relies on point-to-point connections like CAN or K-Line. |
| Data Transfer Speed | Supports high-speed transmission surpassing USB or serial, crucial for large data needs. | Limited by slower rates, leading to longer diagnostic times. |
| System Compatibility | Integrates with modern vehicle electronics and telematics systems, supporting ADAS and OTA updates. | May require bridging hardware for newer systems. |
| Scalability | Adapts to small garages and large plants with minimal infrastructure changes. | Scaling needs extensive hardware, reducing flexibility and raising costs. |
| Operational Cost | Reduces labor and hardware costs by minimizing physical diagnostic setups. | Higher ongoing costs due to manual testing and physical connections. |
DoIP not only meets the current demands of vehicle diagnostics but also anticipates future needs with its scalable, efficient, and flexible capabilities.
Compared to traditional protocols, DoIP is more adept at handling the sophisticated diagnostics required by modern vehicles, making it a strategic investment for the future of automotive technology.
AutoPi DoIP Solution: Enhancing Vehicle Diagnostics
The AutoPi device leverage DoIP technology to enhance automotive diagnostics and firmware updates with our state-of-the-art fleet maintenance solutions, which are designed for seamless integration and superior performance.
Our key features include real-time diagnostics, which allow for immediate detection and resolution of issues without causing vehicle downtime. We also offer over-the-air updates to ensure that vehicle software is always updated efficiently using DoIP’s robust network capabilities. Additionally, our solutions are equipped with advanced security protocols that protect data during transmission, enhancing data security across all operations.
-
Modern vehicles, increasingly burdened with complex electronics and software, face heightened vulnerabilities; AutoPi's DoIP solution addresses these concerns.
-
Utilizes Ethernet for faster, more reliable remote diagnostics and ECU flashing, enhancing both speed and reliability.
-
DoIP, a critical protocol software for modern automobiles, revolutionizes ECU diagnostics by leveraging faster and more reliable communication channels.
-
Compliant with ISO 13400 standards, our DoIP solution is ready-to-deploy, enabling quick implementation of remote vehicle diagnostics tailored to specific production needs.
For further details on our DoIP capabilities and integration:
-
Visit our documentation page.
-
To discuss custom diagnostic services or specific requirements, please contact us.





